Using soluble 3D printer filament to build support structures
Using soluble 3D printer filament is an easy and effective way of building support structures for your 3D printed part. In this article, we run through the different types of soluble filaments on offer, the advantages of using this type of material as opposed to insoluble supports, and our tips and tricks for the smoothest printing process possible.
3D FDM printing is a manufacturing technology that allows us to create parts with complex geometries, typically impossible to achieve using traditional methods. However, in using this technology, each layer of the part requires a support surface, either on the structure of the part itself or an added support structure.
On single extruder printers, you are limited to using the original printed part’s material to build the support structure. This is not the case in dual extruder printers as soluble filaments can be used to create these structures.
Types of filaments for soluble 3D printing
3D printer water-soluble filaments
These materials are known for being soluble in ordinary water without any type of aggregates. This makes them an excellent option as their dissolution does not represent any type of danger as well as not causing any reaction to the material of the piece.
Of these materials, we have PVA, which is the most commonly used material to create support structures in 3D printing. BVOH is another commonly used material with better material compatibility than PVA as well as a shorter dissolution time.
3D printer water-soluble filaments with chemical agents
Certain materials used at an industrial level are not compatible with filaments such as PVA or BVO due to their chemical properties and/or thermal resistance. For this reason, materials similar to BVOH or PVA have been designed with added properties to allow their compatibility with high-temperature materials such as PEEK, PEKK, PPSU, PP, among others.
To dissolve these support structures, the pH of the water must be acidic in order to break down the sugars this type of material normally contains as this is less dangerous than the use of solvents.
3D printer soluble filaments with organic solvents
These are the least used materials due to the complexity of using organic solvents with the polymers most used in 3D printing because the solvent can react with the print´s material and damage it.
The advantage of using these filaments is that they are highly compatible with the structural material. The most used example being HIPS as a support material for ABS.
Insoluble vs soluble 3D printer filament supports

Soluble filaments for support structures have the following advantages and disadvantages compared to the use of insoluble filaments:
Easier to remove supports
As the support structures are soluble, one simply needs to submerge the piece in the correct solvent and wait for the support structure to disappear. This is highly beneficial to parts with very complex structures.
Improved surface quality of the contact surface
This is an advantage related to the first point; Because the material is easy to remove, it is possible to create a solid base in the area where supports are required, thus allowing a smooth surface finish free of filament remainders.
Less need to post-process the part
The ability to print complex parts with high surface quality due to the use of soluble filaments, also reduces the need to perform post-processing tasks, such as polishing, sanding, gluing, among others.
Longer print times
The problem with using soluble filaments is the increase in printing time, as it is necessary to change materials during printing. However, there are support structure optimization techniques to reduce this problem.
Tips to create support structures with 3D printer soluble filaments
Modifying some settings in your slicer, you can get strong support structures to improve the quality of your printed part. If you want to know more about our slicer, please visit our website about BCN3D Stratos.
Improving the resistance of the support towers
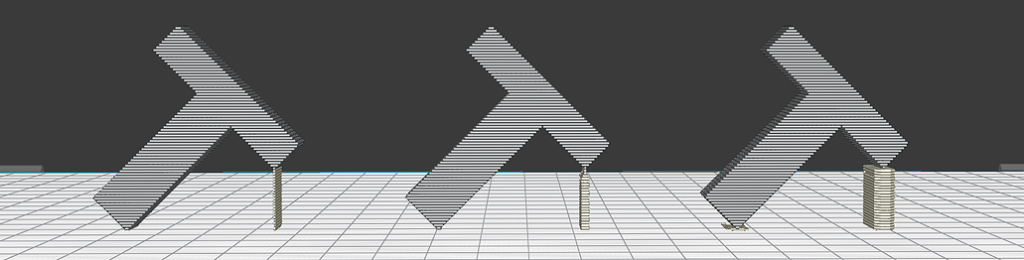
It is quite common for thin towers to be generated to hold very thin parts of the piece, however, they are not resistant and tend to break during the printing process.
To improve the strength of the towers, the following support configuration parameters can be adjusted:
- Horizontal expansion of the support: Increases the overall thickness of the support, allowing the tower to be thicker and stronger.
Avoiding support breakage during the print
The supports have the thickness of the diameter of the hotend, so they are usually quite brittle and can break during the print. By modifying the pattern and other parameters, the robustness of the supports can be increased:
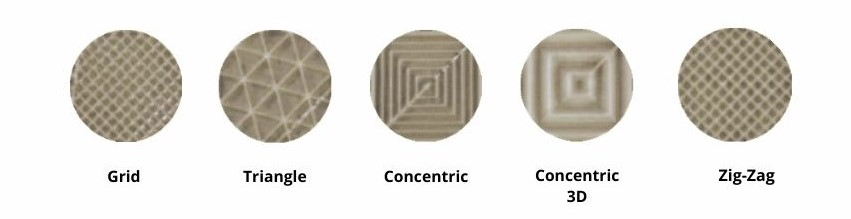
- Support pattern: The grid and triangle patterns are quite resistant to tearing during the printing process. These patterns are only recommended to be printed on soluble material, as they are quite difficult to remove.
- Support printing speed: If the supports are printed too fast there is a risk of the structure breaking. By reducing the speed, the structure avoids vibrations or being damaged by the passage of the head.
Improving the surface quality of the part

The quality of the contact surface depends on the Z distance from the backing pattern, the direction of the top and bottom lines of the perimeter, and the amount of material holding the base of the part. Modifying these parameters can improve the surface quality but complicate the process of extraction of the supports.
- Support density: The higher the density of the supports, the better the piece will hold and therefore the surface finish will improve.
- Top/bottom Line directions: Changing the direction of the perimeter pattern helps to hold the bottom piece layer, as it allows the backing and perimeter patterns to better intersect.
- Support pattern and top/bottom pattern: The patterns of the support and the perimeters influence how the piece of the supports is fastened, the ideal is that the patterns intersect as much as possible to better fasten the first layer.
Always bear in mind that it’s important to keep your filaments dry since soluble materials absorb humidity easily and could cause problems during the printing process. For more information on this topic, check out our knowledge base article.
Materials like PVA and the BVOH can be dissolved in normal water. This water can also be heated to reduce the time it takes to dissolve.
We hope that you follow our tips and tricks to achieve improved surface quality of your 3D printed parts and a faster, more efficient process. Check out how Camper is using the dual extrusion system and the water-soluble materials to revolutionize its footwear design process through in-house 3D printing.




