How Flexible is TPU? All About TPU filament
TPU filament is a very unique 3D printing material. If you’re wondering how flexible is TPU, that’s really its main quality, its flexibility. This filament is often the first one users will reach for when they need to make a print with a little bit of give to it.
In this article, we’ll breakdown everything you need to know about TPU, including its technical qualities, benefits, and common uses.
What is TPU Filament?
Index
TPU filament stands for thermoplastic polyurethane. BCN3D’s TPU is matte and comes in black or white. The most notable property of this filament is its flexibility. Beyond its flexibility, TPU is also very durable and hard to break. It can absorb impact well, making it an ideal filament to use if you need a strong material.
The technical properties of this filament include the following:
- Elongation of 450%
- Tensile strength 150 MPa
- Shore Hardness 98A
- Melting temperature 225°C
- Glass transition temperature of 60°C

How Flexible is TPU filament?
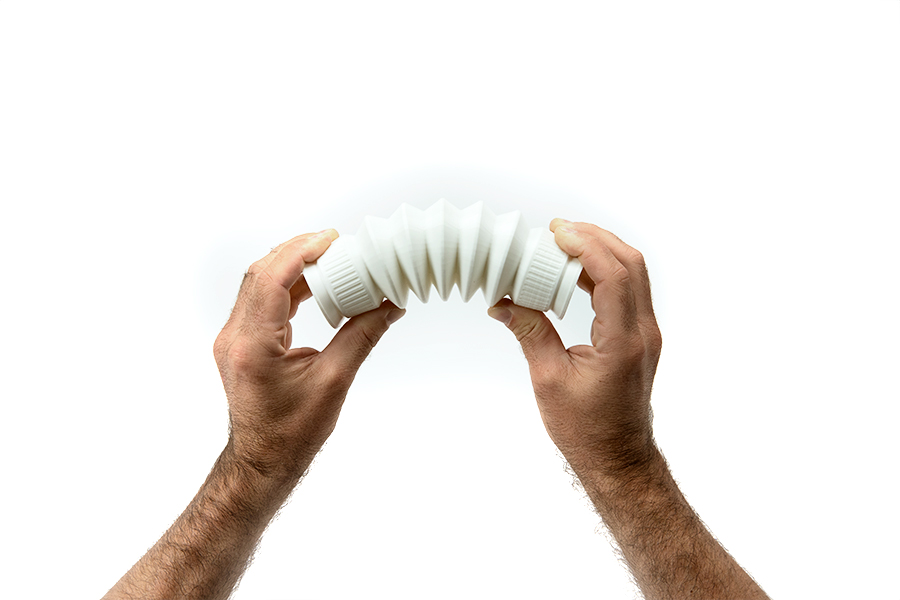
Flexible materials have a property called Shore hardness, which determines the flexibility or hardness of a material. BCN3D’s TPU filament has a Shore-A hardness of 98, making it the most flexible filament in our collection.
So just how flexible is TPU? Generally speaking, its flexibility can be comparable to the analog stick on a video game controller. However, the final flexibility will depend on the features of the object you are printing.
For example, if you print a thin model, you may be able to bend it. But, if you were to print a solid cube, it wouldn’t be as flexible as a stress ball. The way you print your object will impact its overall flexibility.

Common Uses
If you need to print an object that needs a certain amount of flexibility, that needs to bend without breaking, or that needs to withstand a bit of wear and tear, then you should consider TPU filament.
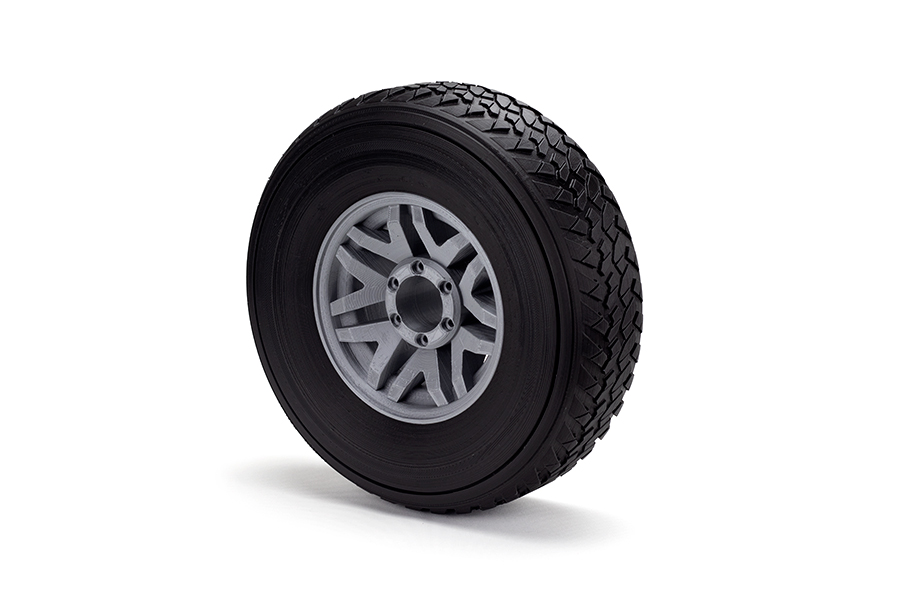
TPU is rubber-like, so it is often used similarly. This means you can create protective cases, non-slip surfaces, wheels, and other objects that you would typically design with rubber. For example, Camper, the popular shoe brand, uses this filament for the soles of their shoe prototypes due to the adaptability of the material.

This filament is also a good option for creating unique tools within a production line, such as seals, gaskets, hinges, handles, springs, and shock absorbers. If you need to build a tool that has to interact with other parts without damaging them, you can also consider using TPU.
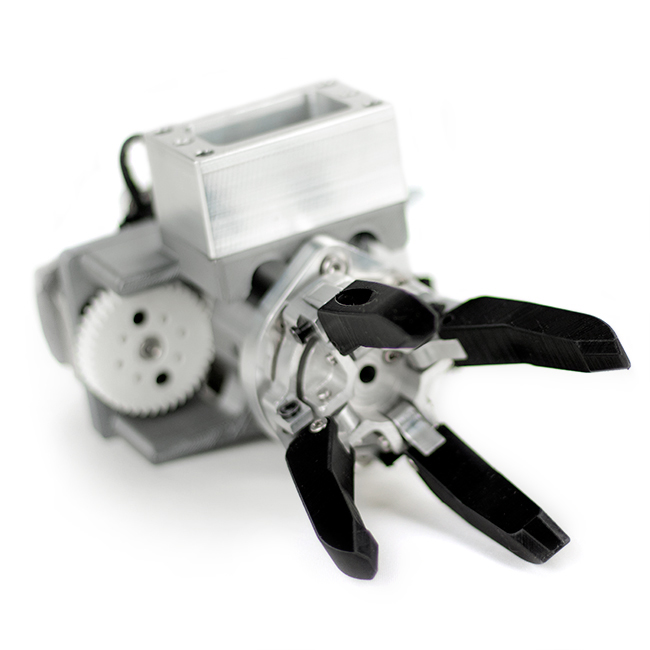
For example, you can create robotic arms that function as a claw. This part will be flexible enough to grab onto objects without damaging or scratching them. This filament can also be used to provide support in an assembly line. Its softness allows it to provide reinforcement without weakening or breaking the original structure.

Its Benefits
As we’ve mentioned, TPU’s main advantage is its flexibility and durability.
- Its alternating hard and soft blocks make it a very resilient material. Its Shore hardness means that it is resistant to abrasion, everyday wear and tear, and high impact.
- The durability of TPU also extends to being able to withstand a variety of elements. This means that it is resistant to water, heat, oil, and certain chemicals.
A disadvantage of this material that shouldn’t be ignored is that it can be difficult to print if you do not have the proper setup. If you are using a printer that does not have a direct extrusion, printing this kind of flexible material will be difficult. However, BCN3D printers do have direct extrusion, meaning that if you are printing TPU with one of our printers, this will not be as much of a concern.
To conclude, this filament has a wide variety of uses and values. If you need to print something that has to be flexible, durable, or resilient, then TPU filament will be your best bet.