3D Flex Filament: Properties, printing process, and purposes
For anyone with a 3D printer, a flex filament can provide some unique advantages to your prints. In this article, we focus on the most flexible filament available in our portfolio: TPU. Let’s take a look at its properties, how to print it, and the different applications made possible by this material.

Printing with a flex filament is nothing to be scared of and opens the door to a wide variety of applications. We focus on our most flexible filament, TPU, how to print it, and some of the interesting applications we’ve seen by manufacturers such as Zoles and Nissan.
Properties of the flex filament TPU
The most flexible material we have in our BCN3D portfolio is TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): a versatile, rubber-like filament.
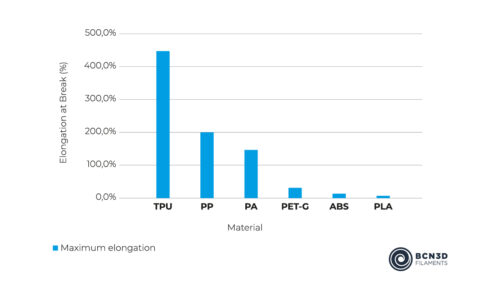
TPU is an elastomeric copolymer, made up of alternating soft and hard blocks, which give hardness and flexibility at the same time. TPU is a thermoplastic elastomer, able to be extended up to 4.5 times its original size before breaking. Its exceptional elongation at break and strength makes this material superior to most filaments. With a Shore-A hardness of 95, TPU is a resistant material for several industrial applications, both mechanical and chemical.
As well as this incredible balance between flexibility and strength, you can expect:
- High resistance to abrasion, wear, and tear
- Great resistance to oils and chemicals
- Excellent impact resistance
- Maximum elongation of 450%
- Withstand operating temperatures up to 60°C
- Compatible with PVA support

How to print
If you’re used to printing with other materials, printing with a flex filament will be no different. Nevertheless, we have some recommendations to ensure you get the best out of these types of printed parts.
- Store it in an airtight container with desiccant.
- Dry the filament before printing by placing it in an oven or in a dehydrator at 60-70ºC for 6 to 8 hours.
- Be sure to have a proper printing profile for TPU using the ones integrated into the BCN3D Stratos. We also recommend sequential printing (one object at a time) because travels leave residual material.
- Finally, as always, use Magigoo to ensure good bed adhesion!

To find out how to increase the flexibility of your parts even further, have a look at our knowledge base article.
What can you use this type of filament for?
Prototyping
Shoe insole manufacturer Zoles is the perfect example of putting TPU to good use. Using an online platform, Zoles’ customers can create their very own customized shoes and insoles with the perfect fit by inputting images of their feet. Using TPU means that the insoles can easily bounce back and forth into shape and cost 50% less than a pair of orthopedic insoles.

Automotive industrial parts
Automotive giant Nissan puts its trust in 3D printed parts along its manufacturing line. Amongst its array of tools, jigs, and fixtures you can find TPU used for:
- This roof upholstery protection tool is anchored to the upper pillar of the car when inserting the car floor carpet. The part protects the roof upholstery from any breakage caused by the insertion of the carpet. Without this tool, subsequent damage to the upholstery subsequently would entail a recovery job with many hours of rework would be required.

- This windshield centering gauge fixture functions as a gauge to ensure the correct distance between the A-pillar of the car and the windshield. Conveniently, the securing of the distance between one side automatically secures the other.

For a closer look at the 3D printed parts in Nissan’s production line, download the full inventory below.
3D printing is edging its way more and more into the fashion industry. ZER Collection uses flexible materials such as TPU to guarantee the functionality of all garments and combine them with materials with different properties such as elasticities and thicknesses.

And many other interesting places…
- Industrial seals, gaskets, sleeves, or hinges
- Soft-touch multi-material models or handles
- Flexible-joined multi-material models
- Protective cases, shoe soles, non-slip surfaces
- Springs, seals, and shock absorbers
- Wheels and rollers
Flex filament can be an asset to anyone considering manufacturing parts for the aforementioned applications…and more! If you’re yet to try it, we hope that this article has convinced you that it can add a lot of value to your 3D printing experience. Should you need any more 3D printing tips and tricks, visit our BCN3D knowledge base.